Dental Bone Graft
Dental Bone Graft – Overview
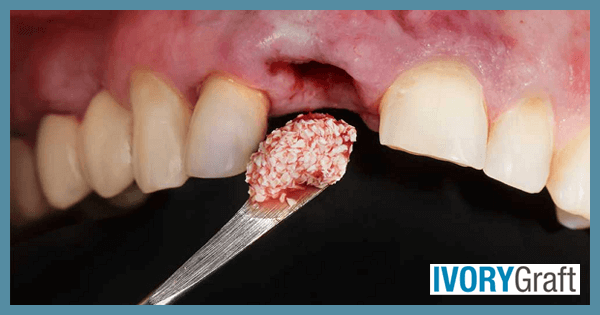
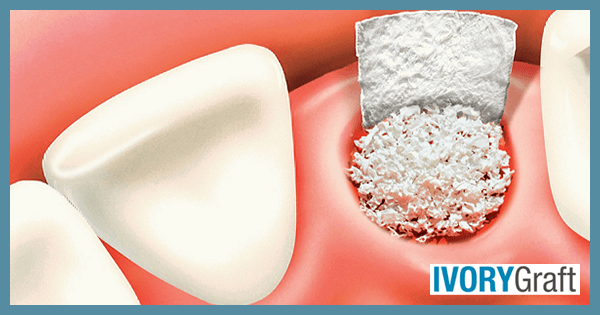
A dental bone graft addresses the common issue of insufficient bone quantity often encountered in routine dentistry. Bone resorption or the development of ridge defects may occur due to factors such as age, infection, trauma, surgery, or congenital malformations.
Read moreDental Bone Graft – Applications
Resorption of alveolar bone is commonly seen in the posterior part of the alveolar ridge. This can cause patients to bring their jaw forward while chewing, leading to an incorrect chewing habit. To avoid this, it is advised to replace missing teeth, and if there is insufficient bone, a bone graft should be used.
Read moreDental Bone Graft – Ordering and audiences
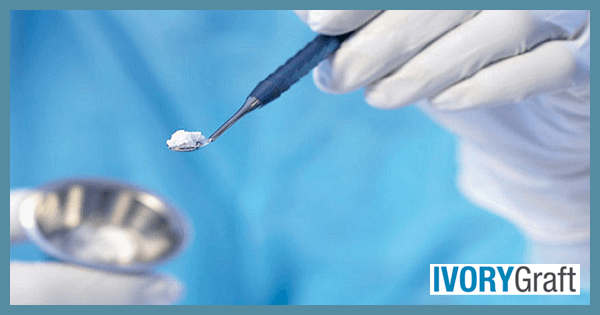
It is crucial to understand the potential benefits and risks of a dental bone graft. The procedure is generally considered safe and well-tolerated by most patients, and with proper care and follow-up, the success rates for dental bone grafts are typically high. However, since it is a surgical procedure, it does involve some risks.
Read moreDental Bone Graft – Procedure
Dental bone grafting is a specialized dental surgical procedure that should be performed by a qualified and experienced dental professional who has received training in this area. Typically, maxillofacial surgeons, implantologists, or periodontists carry out the procedure.
Read moreLoad more articles
Dentin
Dentin – Overview
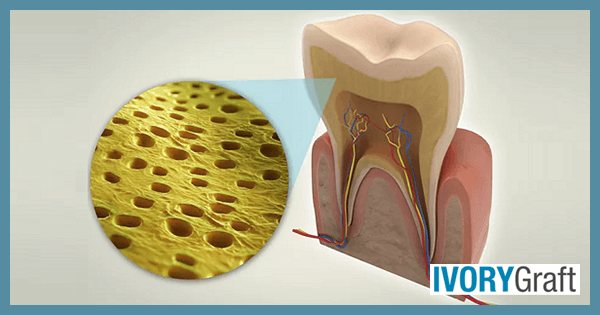
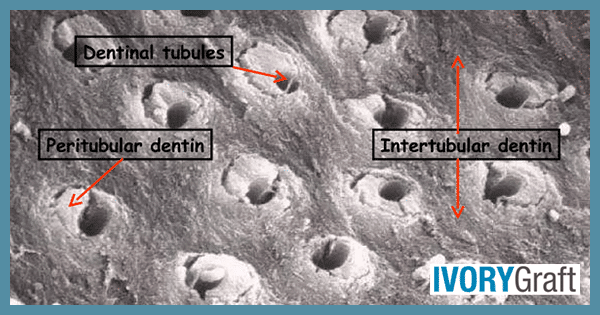
Dentin is a mineralized connective tissue that makes up the inner part of the tooth, enclosing the pulp. It is covered by enamel in the crown portion and cementum in the root. Composed of 45%-50% inorganic or mineralized material, 30% organic material, and 25% water, mature dentin is a crystalline substance.
Read moreDentin – Anatomy and Histology
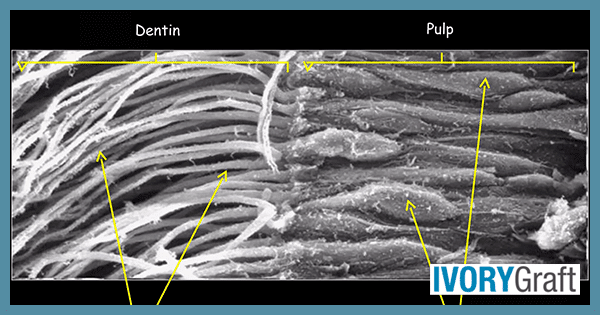
Dentin is a vital, hard, mineralized tissue that forms the bulk of the tooth structure. In the crown portion, it is found between the enamel layer and the pulp, while in the roots, it is found between the cementum and the pulp. Dentin is composed of a dense organic matrix of collagen fibers and hydroxyapatite crystals, as well as small spaces called dentinal tubules that run through the tissue.
Read moreDentin – Growth and Formation
Dentin is a hard, mineralized vital tissue that is formed by specialized cells called odontoblasts. dentin makes up the bulk of a tooth. Odontoblast is located in the pulp of the tooth. Throughout life, the growth of dentin occurs continuously, as the odontoblasts lay down new layers of dentin on the inner surface of the existing dentin.
Read moreDentin – Hypersensitivity
Dentin hypersensitivity is a common dental condition characterized by sharp, transient pain or discomfort in response to external stimuli such as hot, cold, sweet, or acidic substances, or even by physical contact like brushing or flossing. This pain occurs when the dentin, which is the layer beneath the tooth enamel and cementum, becomes exposed due to various factors such as gum recession, enamel loss, or root exposure.
Read moreLoad more articles