- 21 Tuval St.,Diamond Tower, 13th Floor - #1380, Ramat Gan 5252236, Israel
- info@ivorygraft.com
Home / Articles
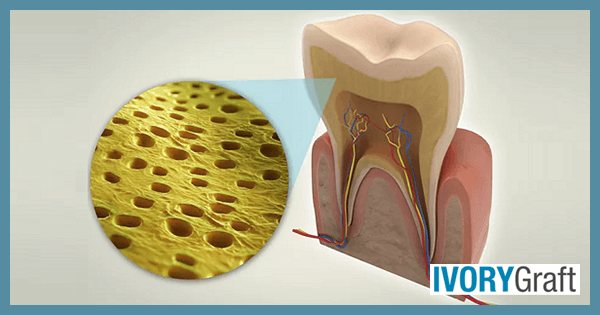
Dentin is a mineralized connective tissue that makes up the inner part of the tooth, enclosing the pulp. It is covered by enamel in the crown portion and cementum in the root. Composed of 45%-50% inorganic or mineralized material, 30% organic material, and 25% water, mature dentin is a crystalline substance.
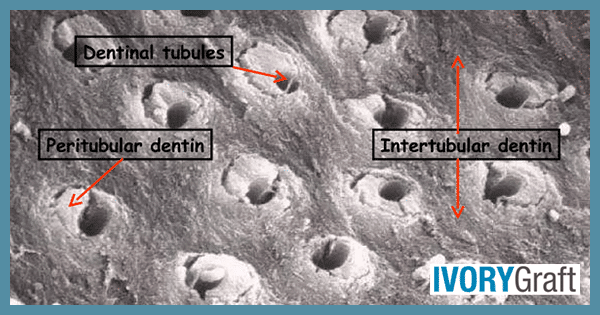
Dentin is a vital, hard, mineralized tissue that forms the bulk of the tooth structure. In the crown portion, it is found between the enamel layer and the pulp, while in the roots, it is found between the cementum and the pulp. Dentin is composed of a dense organic matrix of collagen fibers and hydroxyapatite crystals, as well as small spaces called dentinal tubules that run through the tissue.
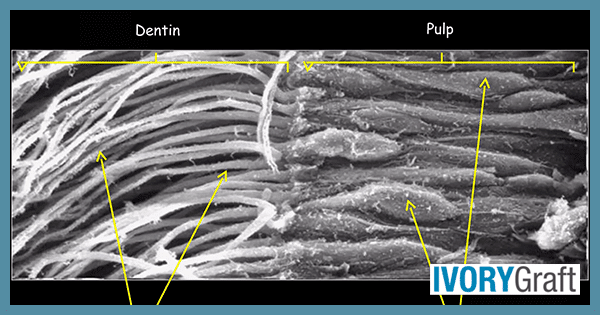
Dentin is a hard, mineralized vital tissue that is formed by specialized cells called odontoblasts. dentin makes up the bulk of a tooth. Odontoblast is located in the pulp of the tooth. Throughout life, the growth of dentin occurs continuously, as the odontoblasts lay down new layers of dentin on the inner surface of the existing dentin.

Dentin hypersensitivity is a common dental condition characterized by sharp, transient pain or discomfort in response to external stimuli such as hot, cold, sweet, or acidic substances, or even by physical contact like brushing or flossing. This pain occurs when the dentin, which is the layer beneath the tooth enamel and cementum, becomes exposed due to various factors such as gum recession, enamel loss, or root exposure.
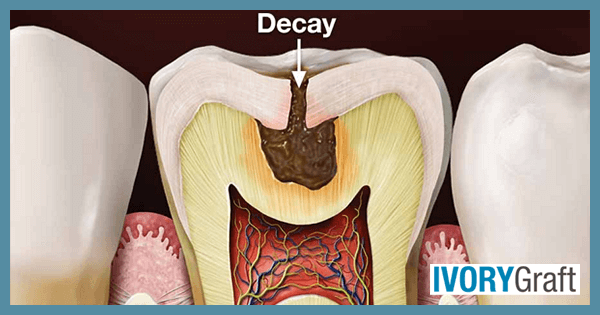
Dentin decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, occurs when the dentin layer of the tooth becomes compromised by the demineralization process, which is caused by bacteria-produced acids. The primary cause of dentin decay is the buildup of dental plaque, a sticky film composed of bacteria, food particles, and saliva. Bacteria in the plaque metabolize sugars and carbohydrates, producing acids that erode tooth enamel and dentin.
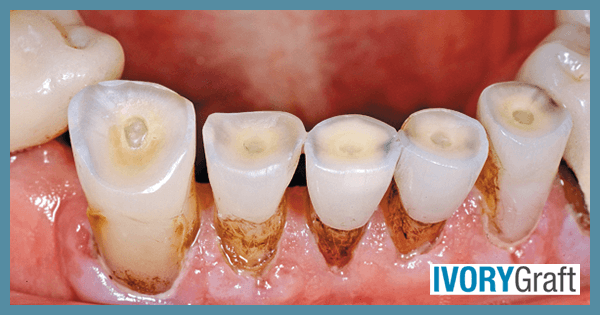
Dentin exposure and tooth wear are closely related dental issues that can affect an individual’s oral health and overall well-being. Tooth wear can affect both the enamel and dentin layers, but dentin is more susceptible to wear due to its lower mineral content and increased porosity compared to enamel.